Introduction The SpokenMedia Project is developing a software application suite/web-based service that automatically creates transcripts from academic-style lectures and provides the basis for a rich media notebook for learning. The system takes lecture media, in standard digital formats such as .mp4 and .mp3, and processes them to produce a searchable archive of digital video-/audio-based learning materials. The system allows for ad hoc retrieval of the media stream associated with a section of the audio track containing the target words or phrases. The system plays back the media, presenting the transcript of the spoken words synchronized with the speaker’s voice and marked by a cursor that follows along in sync with the lecture audio. The project’s goal is to increase the effectiveness of web-based lecture media by improving the search and discoverability of specific, relevant media segments and enabling users to interact with rich media segments in more educationally relevant ways.
Where does it fit in? The system is envisioned as a service that can be integrated directly into individual campus podcasting solutions; the architecture of the system will be flexible enough to integrate with existing workflows associated with lecture recording systems, learning management systems and repositories. The service is intended to plug-in to the processing stage of a simplified podcast workflow as illustrated below. A goal of this project is to integrate the system as part of a Podcast Producer-based workflow using an underlying Xgrid to perform the automated speech recognition processing.
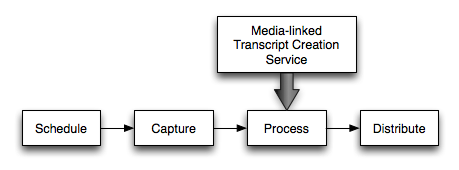
(Simplified) Workflow with Transcript Creation
How does it work? The process for creating media-linked transcripts, as illustrated below, takes as inputs the lecture media, a domain model containing words likely to be used in the lecture, and a speaker model selected to most closely match the speaker(s) in the lecture. The output from the speech processor is an XML file containing the words spoken and their time codes. The time-coded transcripts and lecture media are brought back together and are viewable through a rich media browser.
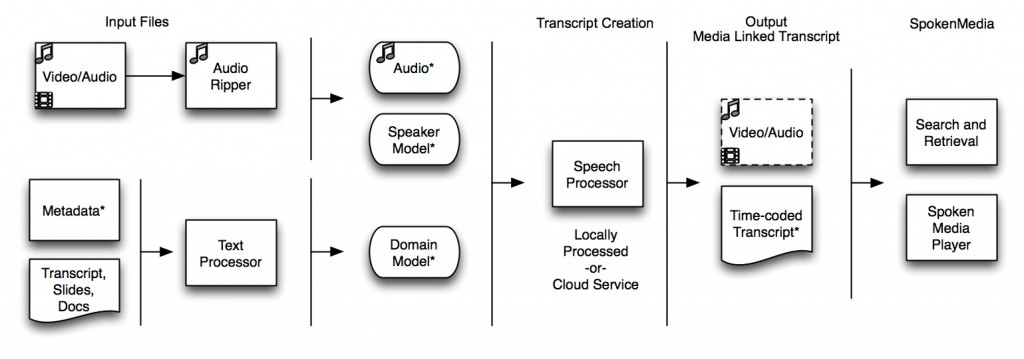
SpokenMedia Workflow
Key steps in the workflow include the use of a collection of texts, such as lecture notes, slide presentations, reference papers and articles, that are processed to extract all key words and phrases to form a domain model. The creation of individual speaker models (such as from faculty teaching term-long courses) increases the accuracy of the recognizer and therefore transcription accuracy. The speech processing is multithreaded to process audio file segments in parallel; similar to video processing in existing Podcast Producer workflows, the speech processing is suited for an Xgrid or cloud-based (e.g., Amazon EC2) deployment.
